Vane Shear Test
Need and Scope:
The laboratory Vane shear test is used for the measurement of shear strength of soft cohesive soils. It is useful for soils of low shear strength for which unconfined compression tests cannot be performed. This is a cheaper and quicker test.
Concept:
Shear strength of soft soils for which soil samples cannot be collected in undisturbed state. Vane shear tests are performed either in laboratory or field.
Vane Shear Test
Experimental Setup:
- Vane shear apparatus (Laboratory)
- Specimen inside the vane shear specimen container
- Shear vanes with the torque rod
- Torque applicator
- Torque spring
Testing Procedure (IS 2720 Part 30):
- Prepare four specimens of soil sample of dimensions of atleast 38 mm diameter and 76 mm height in specimen containers (H/D ratio of 2).
- Mount the specimen container with the specimen on the base of vane shear apparatus.
- Gently lower the shear vanes into the specimen to their full length without disturbing the soil specimen. The top of the vanes should be atleast 10 mm below the top of the specimen.
- Start the machine and apply the torque on the specimen by movement of shear vanes. Note the readings of the angle of twist.
- Rotate the vanes at uniform rate of 0.1 degree per second (for example) by suitable operating the torque application handle until the specimen fails.
- Note the final reading of the angle of twist.
- Four tests need to be performed using chosen torque spring with known spring constant.

Vane Shear Test
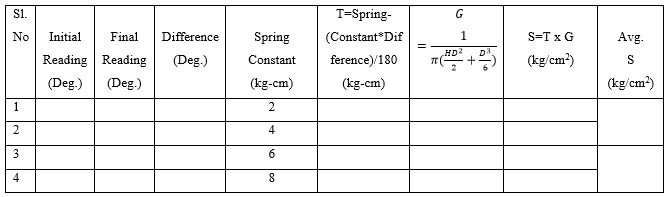
Observation Sheet:
Site location = —————————————
Description of soil sample = ———————–
Height of vane (H) = —————————— cm
Diameter of the vane (D) = ————————cm
Spring constant (K) = —————————— kg-cm
Rotation of Vanes = —————————— deg/sec
Difference in degrees while torque application (δ) = —— deg
Applied Torque (T) = —————————— kg-cm
Shear strength of soil (S) = —————————— kg/cm2

Vane Shear Test
General Remarks
- The Vane shear test is useful when soil is soft and its water content is nearer to liquid limit of soil.
- This test is recommended for soils shear strength less than 25 kPa.
Vane Shear Test
Theory:
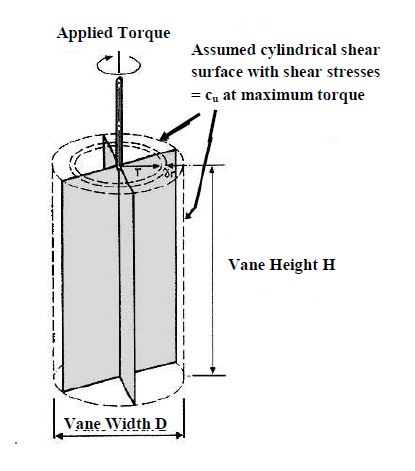
The shear vane consists of four plates welded orthogonally to steel pipe as shown in the schematic diagram.The vane is inserted in soil mass directly in laboratory or in bore hole at the site (for field vane shear) at suitable depth. The applied torque is measured by calibrated torsion spring, angle of twist being read for special gauge.
The vane is rotated quickly enough to ensure that the test is carried out under undrained conditions. The vane shears a cylindrical failure surface, where the shear stress at failure is the same at the upper and lower horizontal circular areas and the vertical cylndrical surface. The calculated torque is the resistance against the shear stresses along these surfaces.
Cylindrical surface:
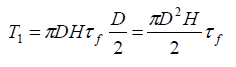
On Circular surface:
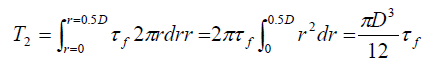
For equilibrium, the torque applied to shear the clay is given by T = T1+2T2:
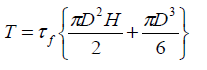
The test being undrained, τf = cu
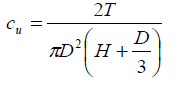
Where:
H = Height of vane
D = Diameter of vane
r = Radius of vane
τf = Shear stress at failure
