MULTICHANNEL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES (MASW)
MASW is a non-destructive seismic method to evaluate material layer thickness, their shear wave velocity (1D (depth) or 2D (depth or surface location)), poisson’s ratio, and density.
Need and Scope:
It is non-invasive technique that can be used for geotechnical characterization of near surface material , which works on the principle of Dispersion of Rayleigh Waves.
Concept:
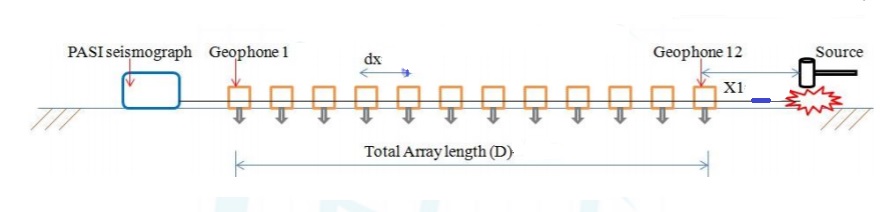
The process involves the generation of surface waves and collection of the same through a network of geophones and data acquisition system (DAS). Surface waves can be generated by an active source such as sledge-hammer or weight drop or can be collected from passive source such as ambient natural, cultural and traffic activities. The records are collected by a multichannel data acquisition system or a seismograph. The geophone receiver array deployed with an appropriate geometrical configuration is connected to the seismograph through a connecting spread cable, which transmits the recorded field data to the seismograph. The multiple receiver system allows collating the characteristics of collected wavefield propagation through the medium.
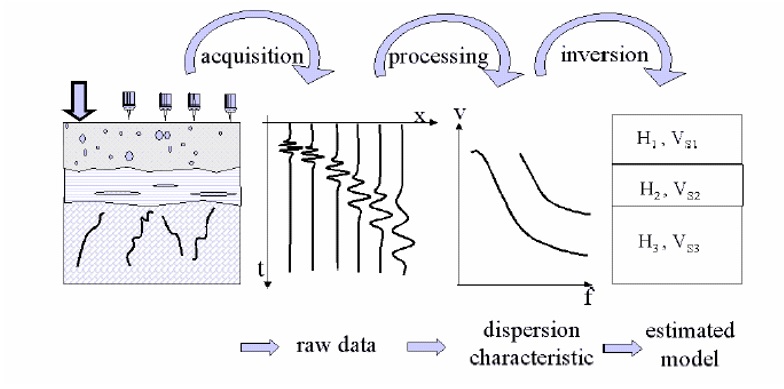
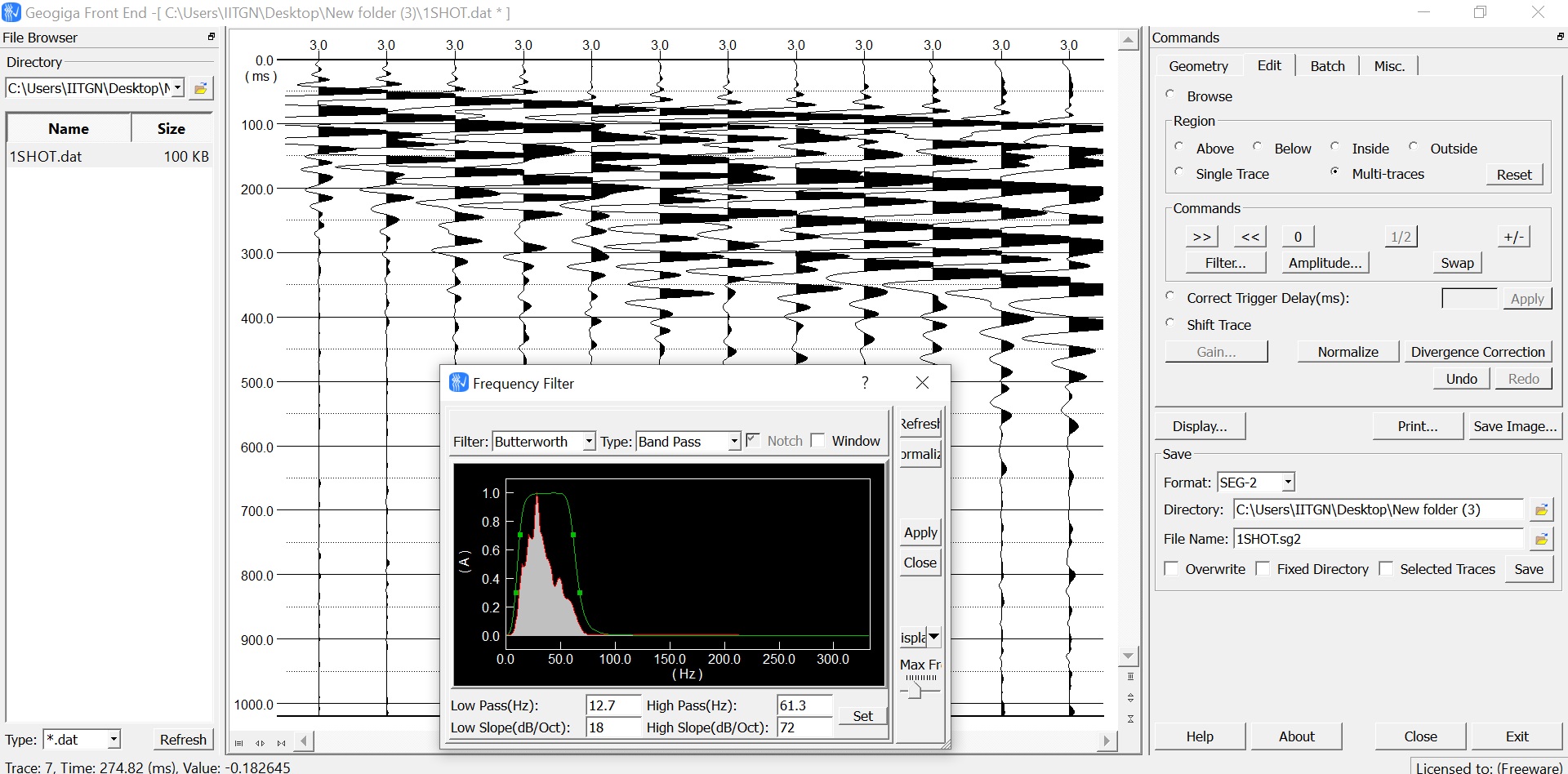
MASW method consist of Data Acquisition, Dispersion and Inversion analysis. Field Data is recorded in the time-domain from 24 geophones, with the help of seismograph. This is done by hammering near the starter geophone. Filtering of time domain signal is performed for the required frequency range of 3 to 50 Hz to ensure that specified geophone frequency (4.5 Hz) lies in this range. Filtered signal, geophones spacing and offset distance validate the quality of dispersion curve (DC) which is the plot of Rayleigh –wave phase velocity and frequency. Picking points for the maximum amplitude at a particular frequency gives trends of fundamental and higher modes. Picking of dispersion mode is done by manual or automatic means, depending upon the dispersive trends. Time domain signal is converted into frequency domain signal using Fast Fourier Transformation (FFT) and Summed amplitude of power spectrum in DC indicates the pattern of occurring mode. The MASW initial model requires several values based on theoretical judgment, such as velocity ratio (Vp/Vs), thickness (h) and density (ρ). This dataset, which produces a theoretical DC is inverted using several iterations to match experimental DC. Error minimization is done using misfit function after several observations in velocity profile. The final model with the least error is chosen as the velocity profile. The use of MASW is increasing being applied to geotechnical engineering for the measurements of dynamic properties, soil profiling, microzonation and site response studies. The measured dynamic properties (Gmax) can be used for the design of structure for earthquake/cyclic loading , settlement analysis and also Vs is widely used in liquefaction assessment.
MULTICHANNEL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES (MASW)
EXPERIMENTAL CONFIGURATION:
The method has two basic modes of surveying
(a) Active MASW
(b) Passive MASW
The depth of investigation achievable via active test is normally in the range of 20-30 m and information of deeper layers of soil in the range of 100-120 m can be achieved via passive test with the help of these mentioned below equipments.
- Geophones receivers of low frequency in the range of 4.5Hz
- DAQ/Seismograph 24 –bit Analog –to-Digital convertor
- Spread cable to connect geophones and seismograph
- Hammer cable for triggering the impact
- Sledge-hammer and striking plate
- WinMASW , Analysing & Processing Software
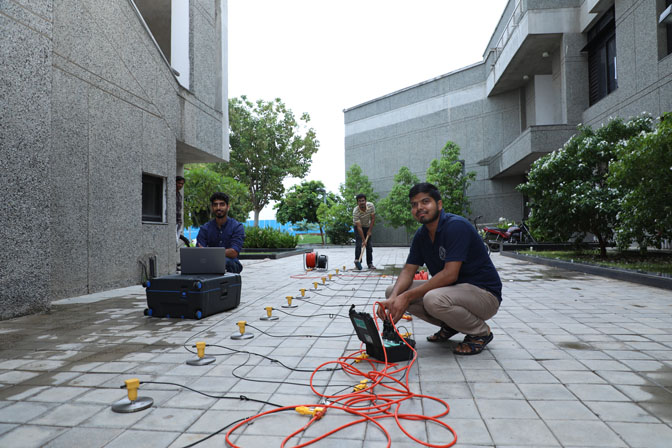

FIG 1- EXPERIMENTING ON THE PAVED ROAD USING METAL PLATES
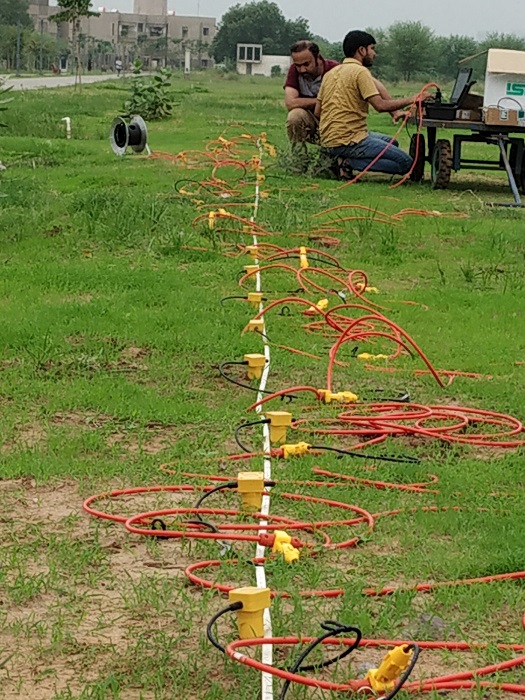

FIG 2- EXPERIMENTING ON THE SOIL SURFACE USING SPIKES
Methodology:
It is a three-step scheme for its processing.
- Data Acquisition : multichannel field records are acquired , which are often called as shot gather or seismic gather, in conventional exploration.
- Data Filtration : Set frequency range of 2 to 50 Hz for 4.5 Hz geophone and filter data using Geo-giga Software.
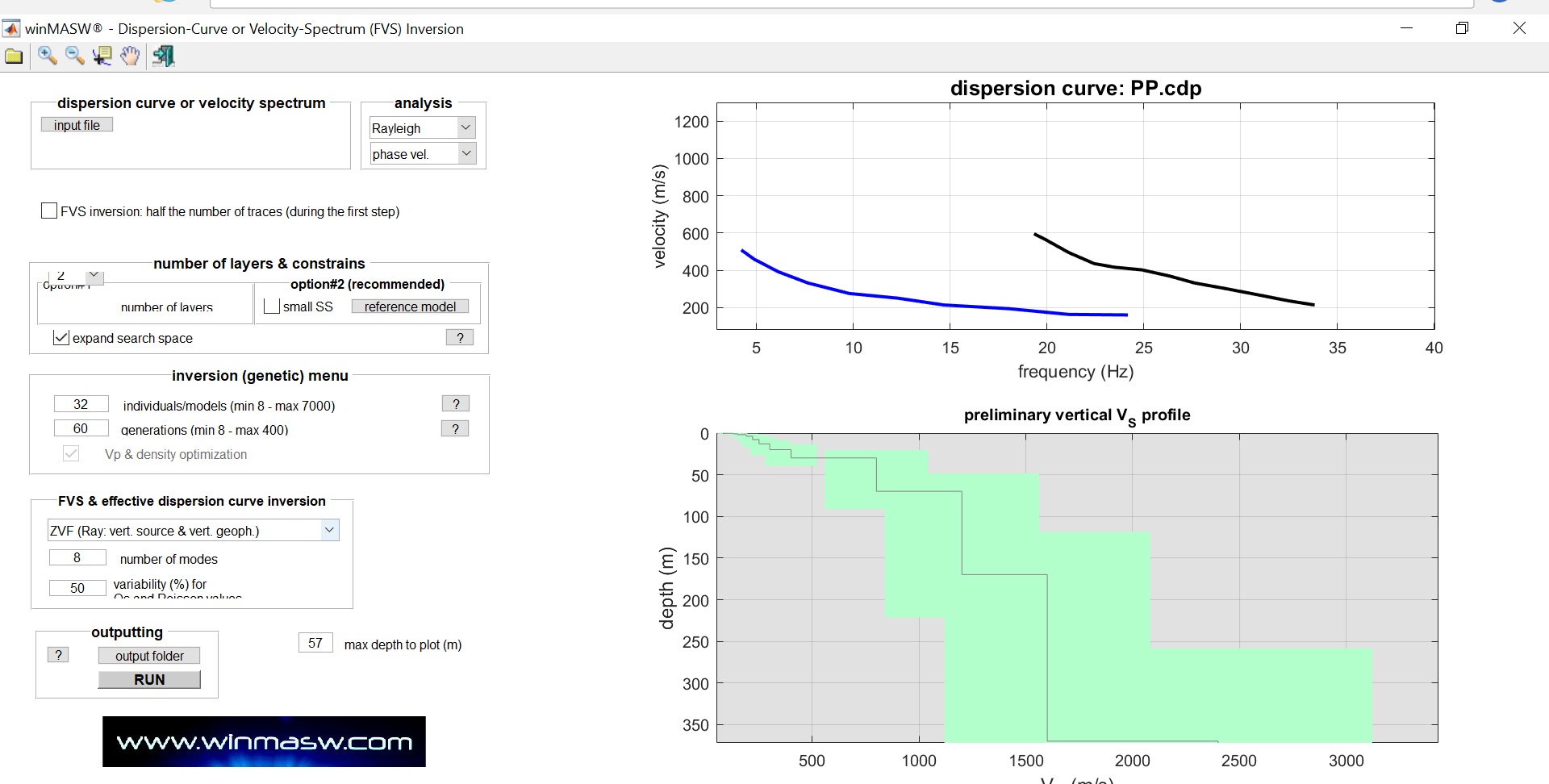
- Dispersion Analysis: the objective of this analysis is to obtain an accurate dispersion curve. In general, dispersion curve is a plot between phase velocity of Rayleigh waves and frequency for a particular mode.
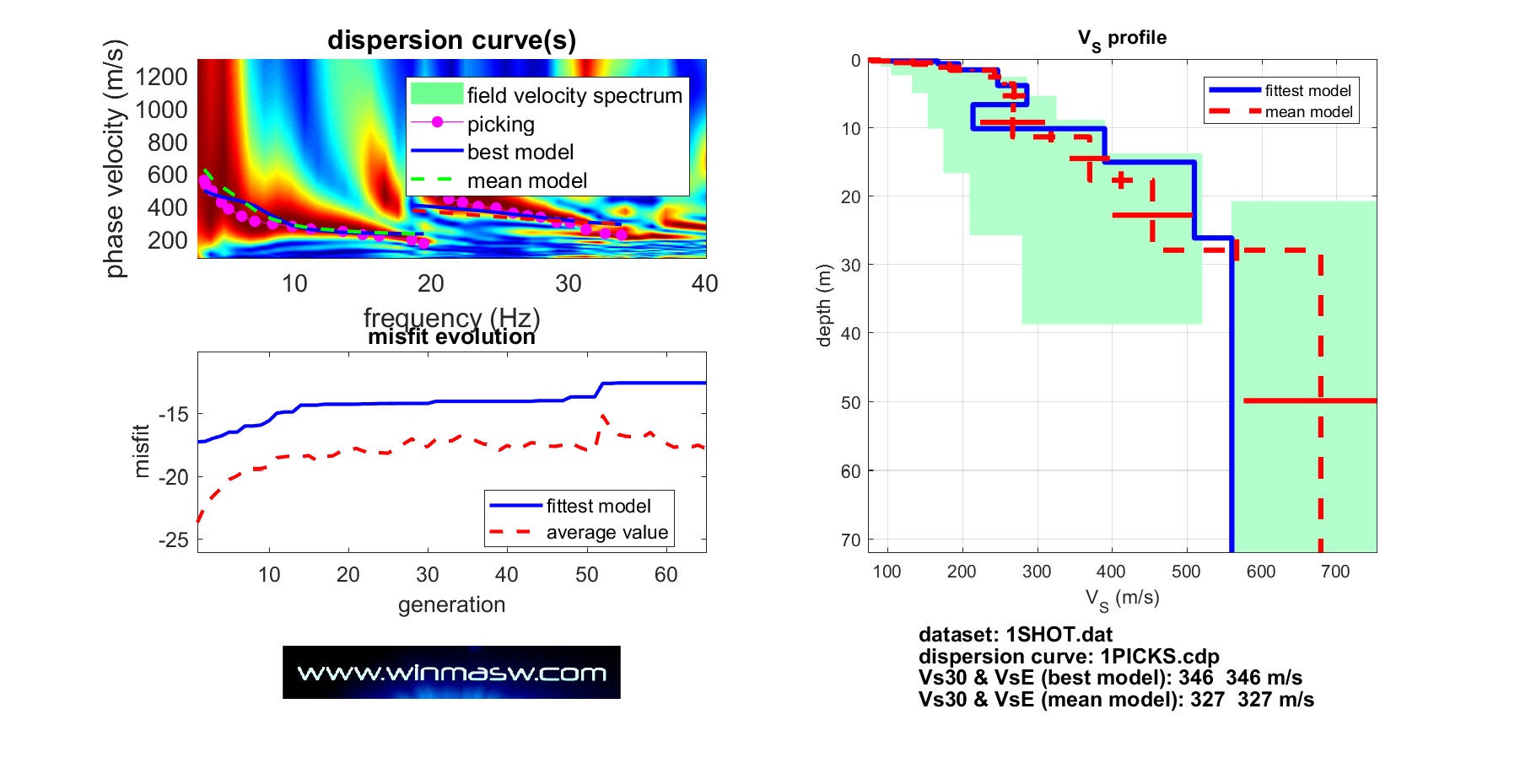
- Inversion Analysis: it is an iterative approach which uses optimization technique to search for the most probable earth model and results the final Shear-Wave Velocity Variation with Depth (commonly termed as 1-D Vs profile).
- Analysis Methodology: WinMASW Platform have been used for the processing of raw field data.
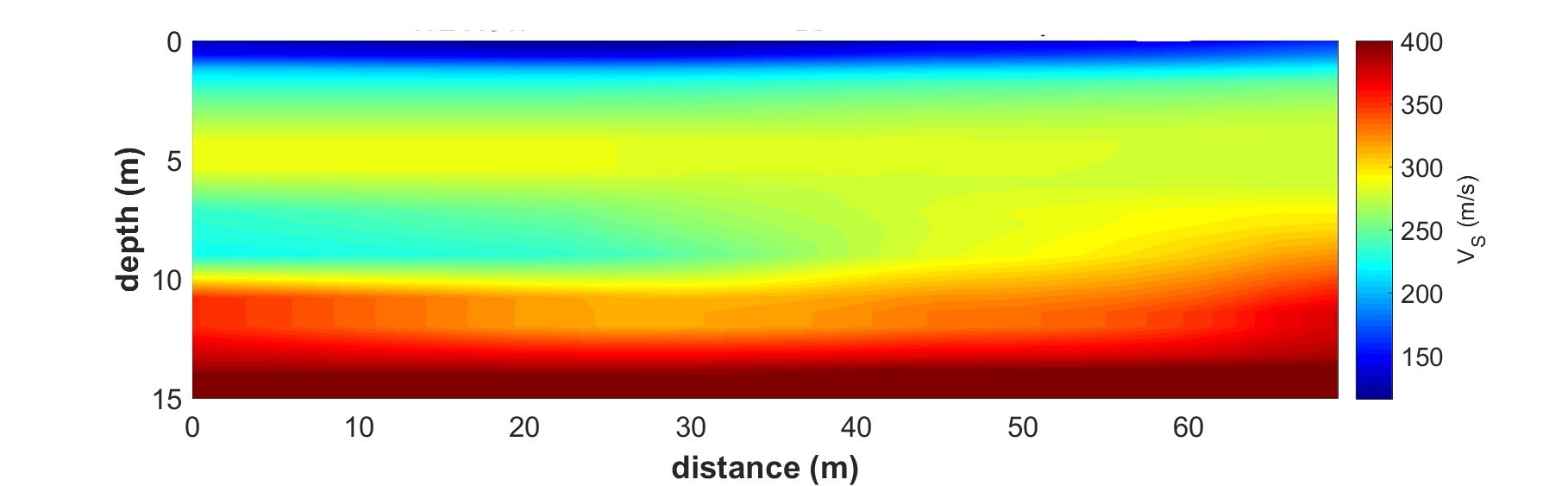
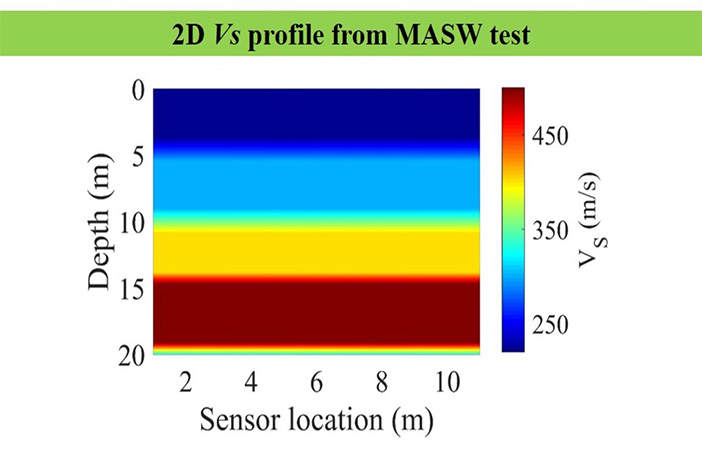
- Interpretation: Overall procedure is to produce multiple 1-D shear velocity profile and combining all we get 2-D shear wave velocity profile. Using 2-D we can interpret soil type, heteroginity , ground anamolies etc.
- Report: software generates the report containing the parameters for ground stiffness like –Vs(shear wave), Vp(phase velocity), poisson’s ratio, Gs(shear modulus) etc.
MULTICHANNEL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES (MASW)
Dispersion Analysis:
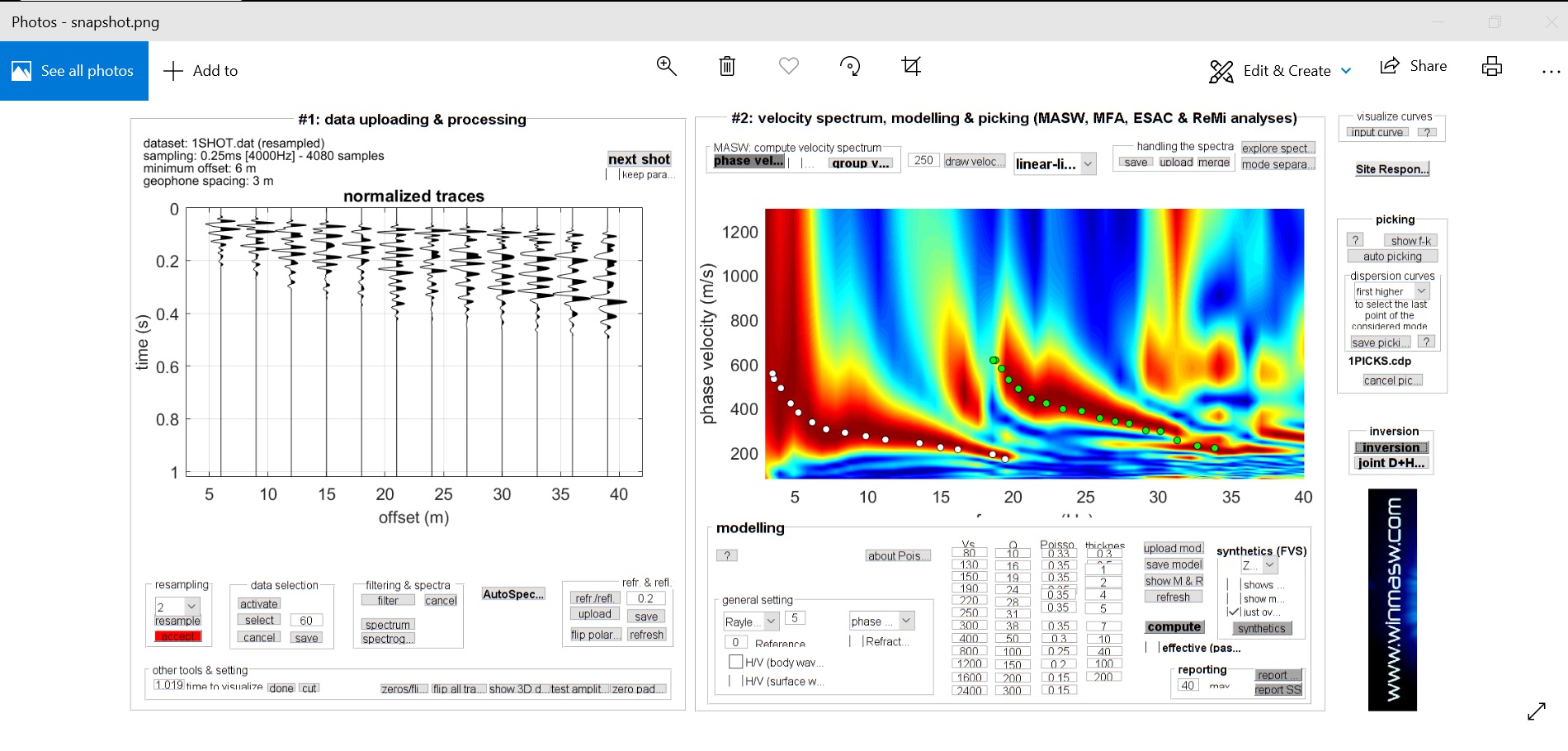
Inversion Analysis:
MULTICHANNEL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES (MASW)
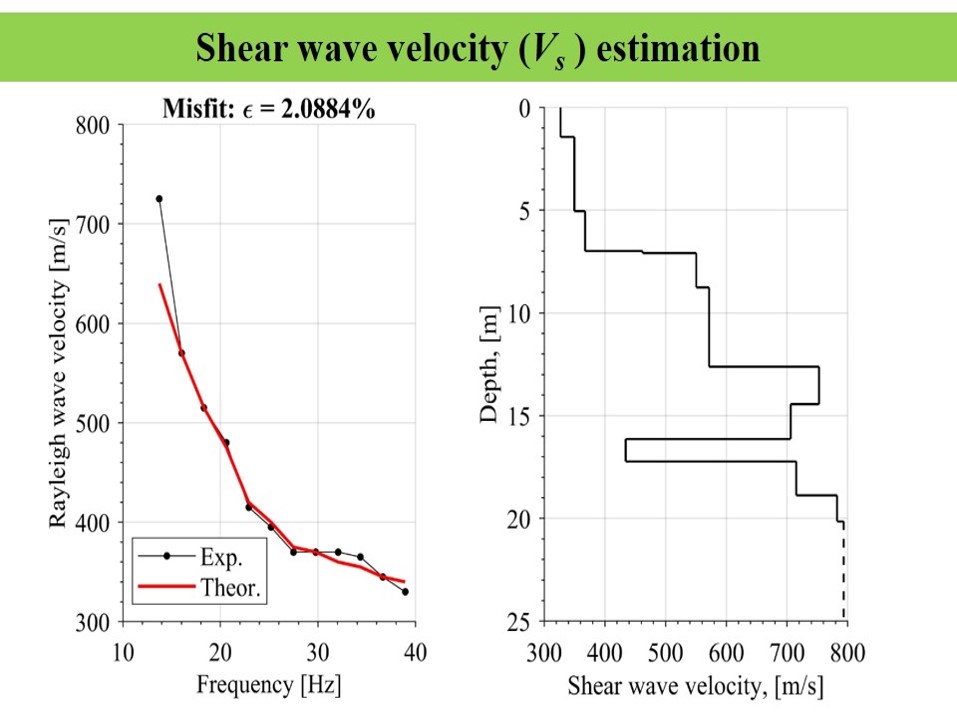
Results:
This output gives the variation of shear wave velocity profile with depth and the correlations can be carried out with ground stiffness like shear modulus(G), SPT value(N) etc. Based on the mode of survey (i) Active(≤30m) or (ii) Passive(upto 100m) it tells about the surface properties.
Limitations:
- Active tests give better resolution in shallow subsurface layers, however, for deeper layer profiling it is ineffective.
- Passive test is capable of investigating deeper layers of subsoil which is quite useful over the active method but although it results poor resolution in shallow layers.
- Near field and Far field effects can only be eliminated by combined use of active and passive test which give broader frequency band and fair resolution both in lower and higher frequency domain yielding confidence in the ultimate Vs profile.
- It is a site specific test so result comparison by other method is also needed.
MULTICHANNEL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES (MASW)
Theory:
Multi-Channel Analysis of Surface Waves or shortly MASW is the updated geophysical method which has been popular surface wave technique of subsoil exploration, attributed to its swiftness and reliability over the techniques. The method utilizes the dispersive characteristics of Rayleigh waves in heterogeneous soil medium and yields subsurface information in terms of Vs profile at the surveyed area. This method can be further used to identify the buried objects and filled up materials in the construction site.
MASW is based on the principle of Rayleigh wave dispersion which is generated by both potential and kinetic energy in active and passive test on the ground surface. Rayleigh waves are produced from the interference of P-waves and vertically polarized S-waves. They travel along or near the surface with low velocity, high frequency(>2Hz) and high energy or amplitude. Particle motion in Rayleigh wave follows Retrogade (anti-clockwise) motion in an elliptical shape ,where the major axis is oriented in the vertical direction. This implies Rayleigh wave travels with different propagation velocities at different frequencies. This property is utilized for obtaining a dispersion curve and finally it is inverted with an efficient algorithm to obtain shear wave velocity Vs profile.
